pleural effusion cat ultrasound
Blood NTproBNP LUS and FCU evaluating left atrial LA size and presence of pericardial effusion PCEFF were performed in all cats. Signs of Pleural Effusion in Cats.

Sonography Assessment Overview Of Afast And Tfast Today S Veterinary Practice
Screening for effusions can be.
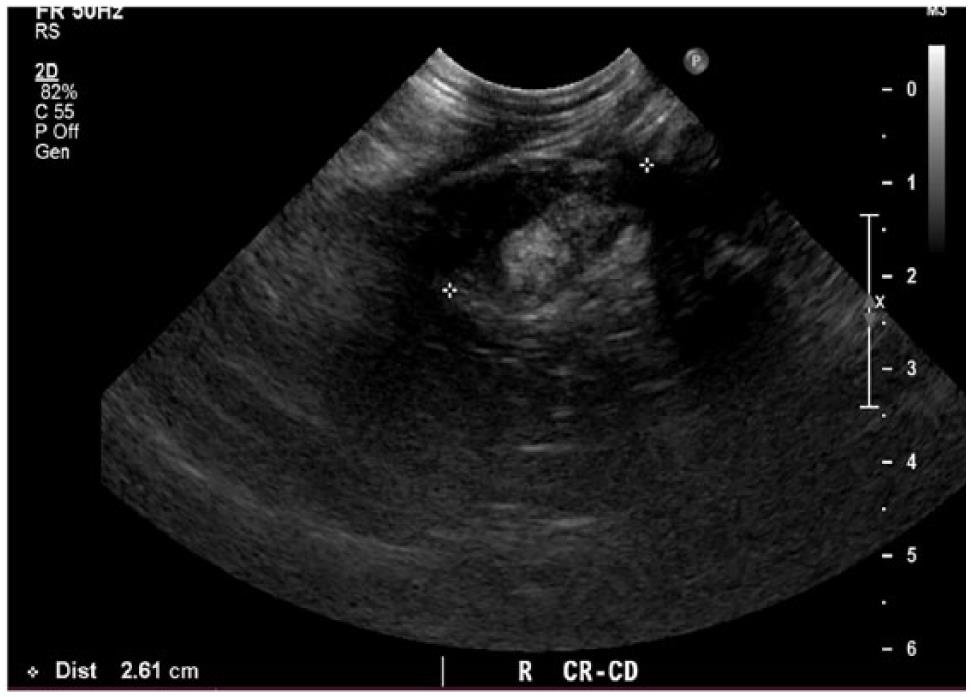
. Diagnostics will be necessary to confirm the cat has pleural effusion and determine a cause. Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. The therapeutic intervention also provides your first diagnostic test.
The aims of ultrasound guided assessment of pleural effusion are. Ultrasound examination of the heart echocardiogram Laboratory tests. To determine and describe the size and site of the effusion.
Focused Assessment Sonography for Trauma FAST procedure. Lung ultrasound and blood NT-proBNP were significant predictors of CHF in a multivariate model. In controlled settings ultrasound may detect constitutive pleural fluid can reliably detect effusions 20 mL in clinical settings and may approach the.
A cat with this condition might show some or all of the following signs. Determining the underlying aetiology is key to appropriate management. To characterize the effusion noting echogenicity of the fluid any loculations solid masses and pleural disease.
Ultrasound is widely considered to be more sensitive than radiography to the presence of pleural effusion in man but this has not so far been reported in cats or dogs1 2 3 It is also often used to subjectively monitor fluid volume in cases of chronic effusion. Medical records were evaluated for final diagnosis. Found with right congestive heart failure obstruction to lymphatic drainage by tissue adhesions in pleural space lung lobe torsion neoplasms and abdominal contents herniating.
Four standard effusion types recognized in addition to blood. Abdominal ultrasounds were performed in 70 cats with pleural effusion and revealed concurrent abdominal effusion in 59 of these cats. The pleural space is the gap between the two feline pleurae which line the lung and aid in breathing.
Measurement of a pleural effusion volume with point-of-care ultrasonography may be a useful tool for intensivists and is an active area of research in critical care 7. Effusions were cytologically. Pleural effusion pocus.
Treatment Pleural Effusion in Cats. A chest ultrasound to look for the presence of fluid within the pleural cavity. Medical records were evaluated for final diagnosis.
Sitting or lying in strange positions to ease breathing. This non-invasive and quick test can help the veterinarian evaluate the cat quickly. Thirty-three of 51 65 cats were diagnosed with CHF.
The lack of specificity is mainly due to the limitations of the imaging modality. For those who are new to imaging around the heart with ultrasound differentiating a pericardial from a pleural effusion can be tricky particularly when the pleural effusion is circumferential around the heart. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing.
Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid of a different nature in the pleural space of cats. Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise. This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the.
All categories of pleural effusion subjectively display as soft tissue opacity on computed tomography CT. 74 dogs and 37 cats with pleural effusion that underwent thoracic CT and diagnostic thoracocentesis were included in the study. In the below clip from the Sonoscape S2 you can actually see the separation of the right ventricular free wall from the pericardium in a cat.
In the following article we present two cases concluding with a third case in which both types of effusion can be seen simultaneously. Pleural effusion is commonly used as a catch-all term to describe any abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. Abdominal abnormalities identified on ultrasound included abdominal masses lymphadenopathy hepatic venous congestion hepatomegaly splenomegaly renal enlargement small intestinal wall thickening steatitis and pancreatitis.
In the latter situations therapeutic intervention must be initiated quickly to prevent respiratory arrest. There is no published method to reliably quantify pleural fluid volume in cats although methods are. Lung ultrasound findings including pleural effusion PLEFF number of B-lines and sub-pleural abnormalities were noted.
Given that most effusions are detected by x-ray which generally cannot distinguish between fluid types the fluid in. When a cat is suffering from pleural effusion the liquid present in the chest cavity prevents the lungs from fully inflating. The treatment of pleural effusion ultimately will depend upon the underlying cause.
Unlike with a pericardial effusion in the case of accumulation of fluid in the pleural space there is no collapse of the heart walls. Initial treatments may vary depending on the likelihood of the specific diseases based on your pets physical examination and history. To mark the optimal site for drainage and perform the procedure if required.
For this reason an abnormal accumulation of fluid in this cavity causes cats to have respiratory distress which. Pleural Effusion in Cats Causes Symptoms and Treatment. Lung ultrasound findings including pleural effusion PLEFF number of Blines and subpleural abnormalities were noted.

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

White Paper Lung Ultrasound In Patients With Coronavirus Covid 19 Disease
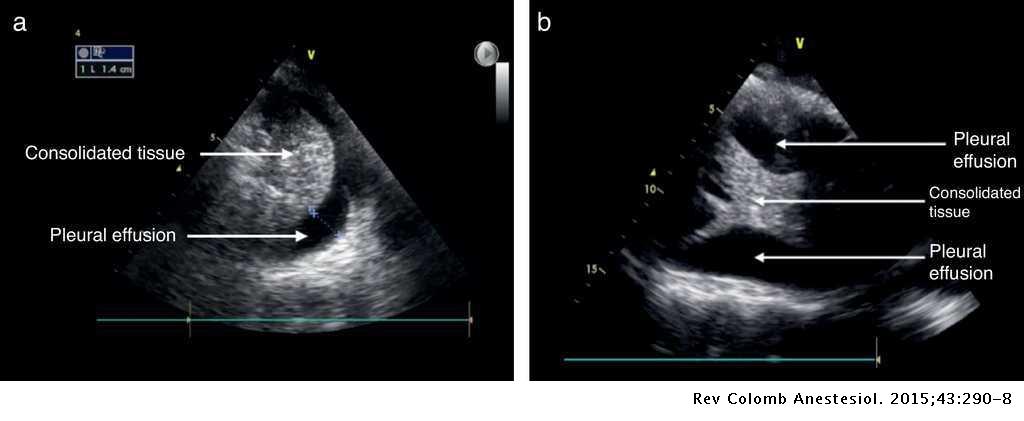
Semiology Of Lung Ultrasonography Dynamic Monitoring Available At The Patient S Bedside Colombian Journal Of Anesthesiology

Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions Animal Ultrasound Association

How To Ultrasound Detection Of Pleural Fluid Case Study Video Youtube

Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat
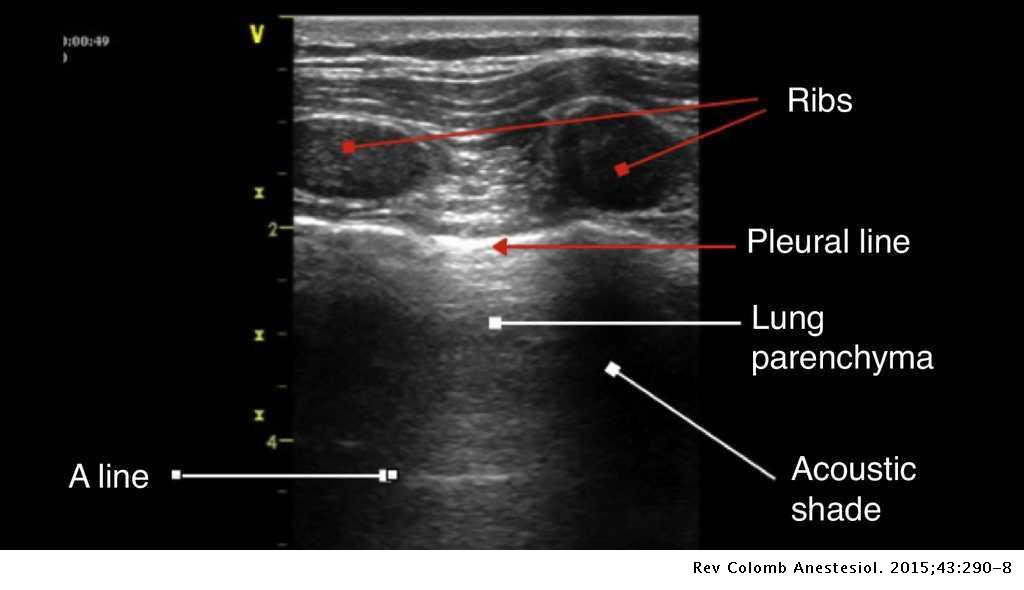
Semiology Of Lung Ultrasonography Dynamic Monitoring Available At The Patient S Bedside Colombian Journal Of Anesthesiology
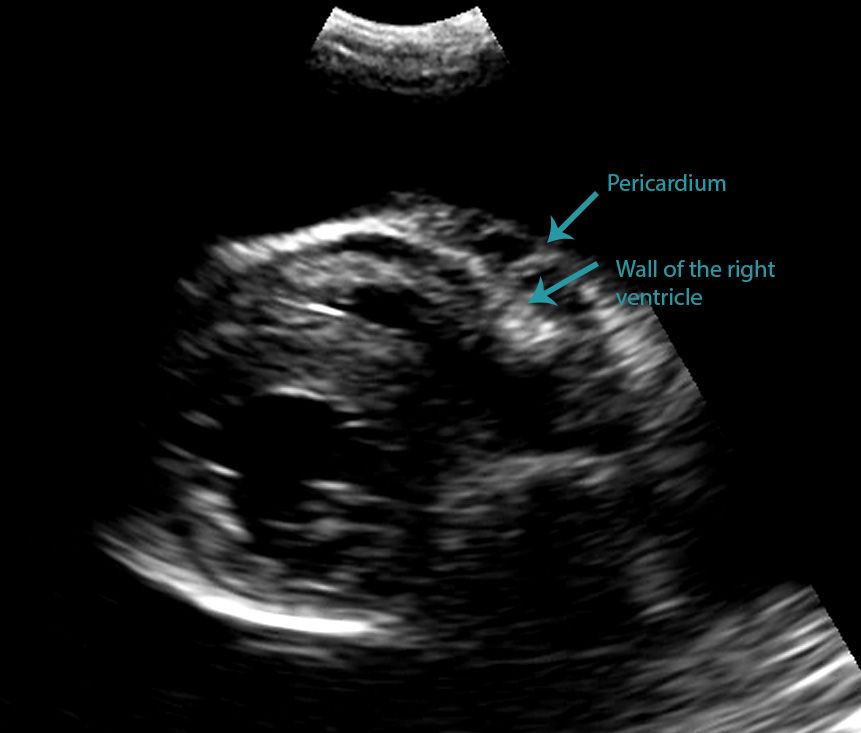
Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions Animal Ultrasound Association

Utility Of Point Of Care Lung Ultrasound For Monitoring Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema In Dogs Murphy 2021 Journal Of Veterinary Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library

Sonography Assessment Overview Of Afast And Tfast Today S Veterinary Practice

The Approach To A Dyspnoeic Cat Cave Veterinary Specialists
Sonography Assessment Overview Of Afast And Tfast Today S Veterinary Practice

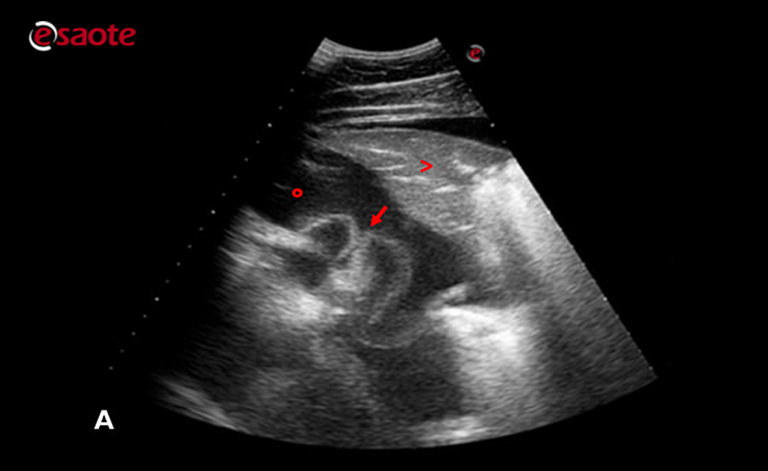
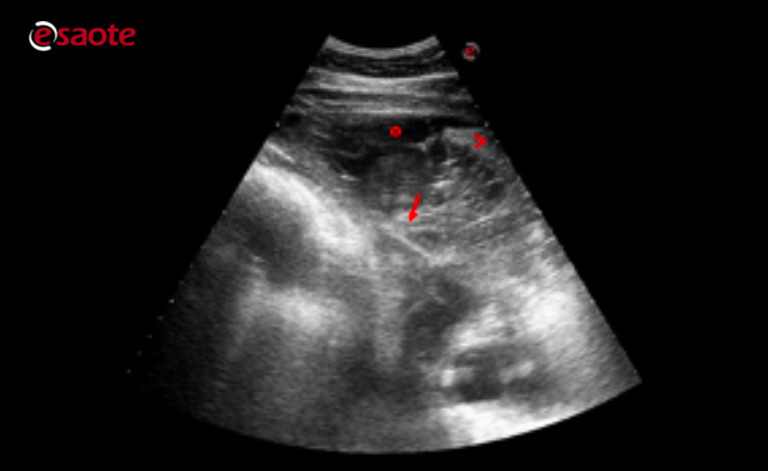
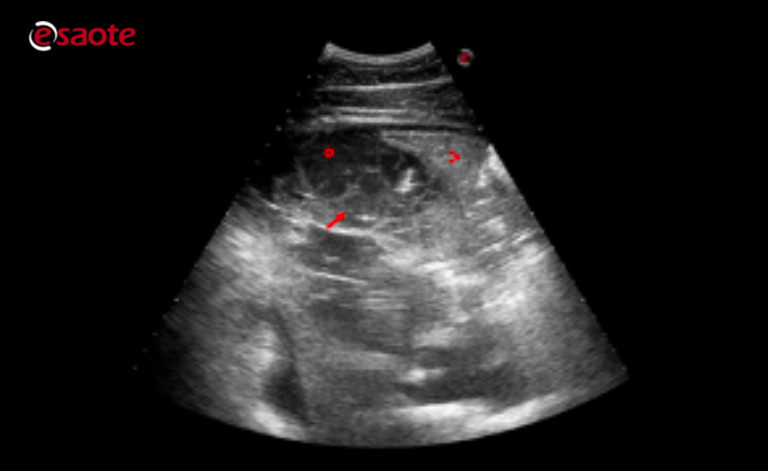
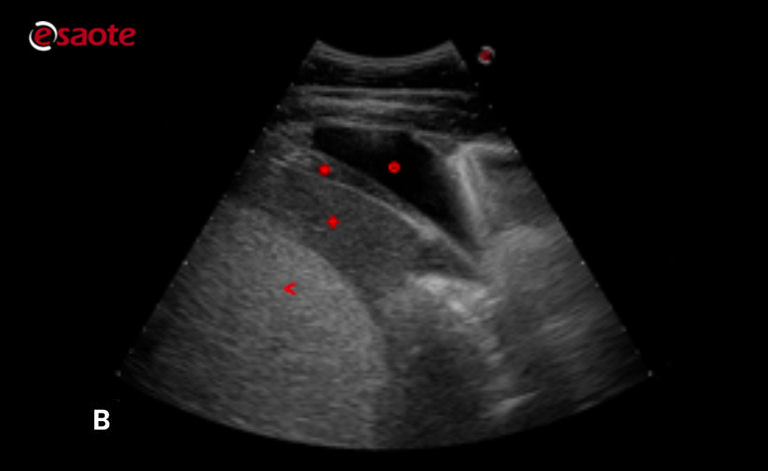
Different Types Of Pleural Effusion On Ultrasound Scan A Exudate B Download Scientific Diagram

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association